
André Fabio Kohn,
Ph.D.
andkohn@usp.br , (andfkohn@leb.usp.br)
phone: (55-11) 3091-5535
E.E.(Electrical Engineering):
Universidade de São Paulo (USP), Escola Politécnica, Dec. 1973 M.S.E.E. : Universidade de São Paulo
(USP), 1976 (research on computerized electrocochleography) Ph.D. : University of California at Los
Angeles (UCLA), 1980 (research on the communication across an
inhibitory synapse in crayfish and in eletronic and
mathematical models) Professor of Biomedical Engineering at
USP Director and co-founder of the
Biomedical Engineering Laboratory at USP Former member of the campus-wide Neuroscience
graduate program at USP Researcher at the National
Institutes of Health (NINDS) from 10/1994 to 4/1995 Research Interests Human Neurophysiology
with Emphasis on the Spinal Cord Modeling and Simulation
of Neurons and Neuronal Networks Motor Control in Humans Clinical Neurophysiology
MS and Ph.D. advisor
I advise students from engineering, physics, computer science and equivalent backgrounds in the Electrical Engineering Program of the Escola Politécnica of
of USP (http://ppgee.poli.usp.br). Papers
and Book Chapters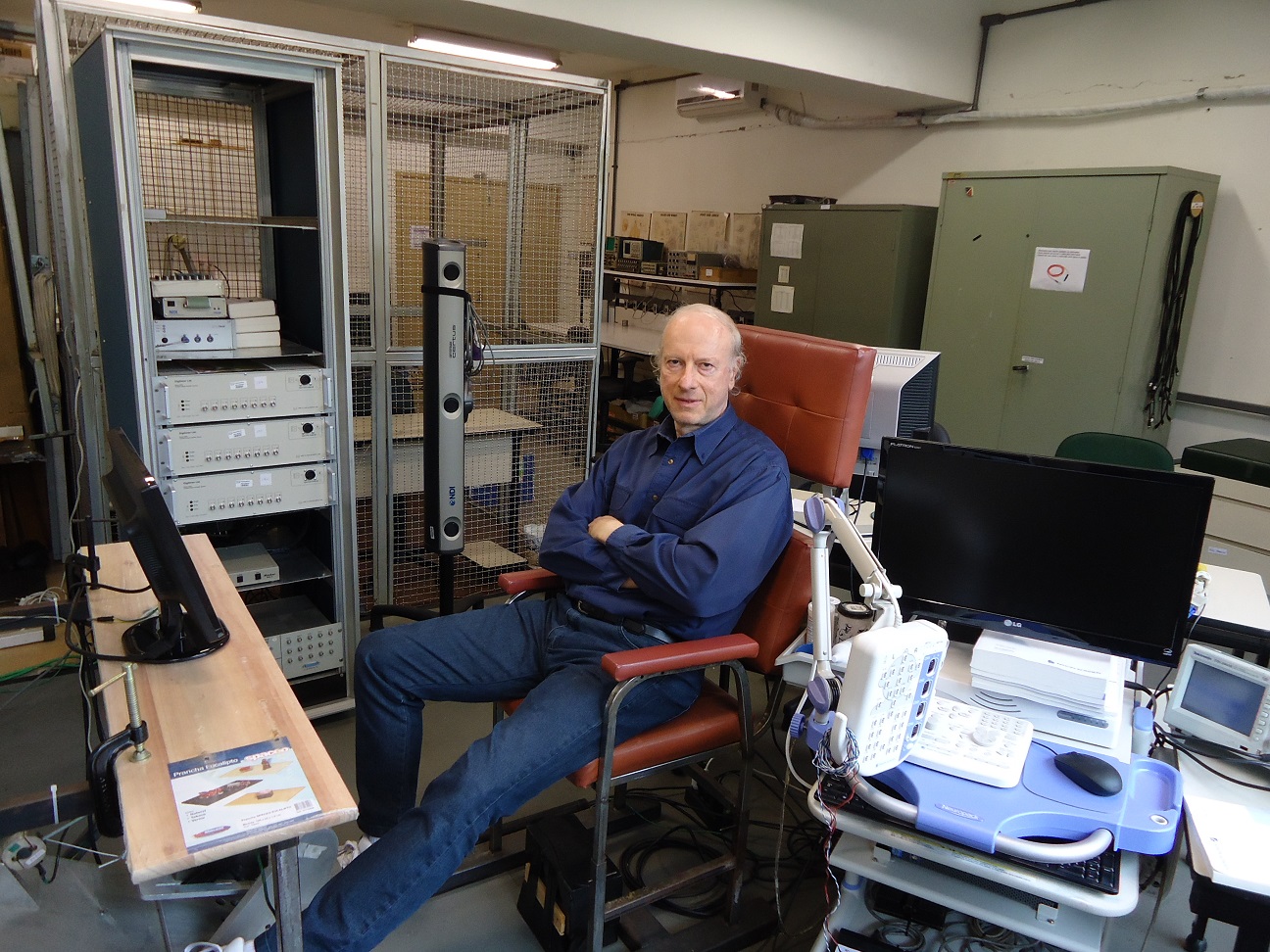 
The main topics of current research include the mathematical modeling of neurons and their networks, synapses, muscles, joints, and the complex interactions of all these elements together. One of the goals is to increase knowledge of the sensorimotor system at different levels of organization. Another topic is the study of postural control in humans by means of experiments using the lab's infrastructure as well as by using appropriate mathematical models. The goal being to further the knowledge on what influences postural control under different conditions.
- J. R. Lara, C. R. Silva, F. F. Lima, M. C. Silva, A. F. Kohn, L. A. Elias, F. H. Magalhães (2022)
Effects of light finger touch on the regularity of center-of-pressure fluctuations during quiet bipedal and single-leg postural tasks
Gait & Posture, Volume 96, Pages 203-209.
- F. F. Lima, C. R. Silva and A.F. Kohn (2022)
Transcutaneous spinal direct current stimulation (tsDCS) does not affect postural sway of young and healthy subjects during quiet upright standing
Plos one, Volume 17, Edição 4, Páginas e0267718, Editora Public Library of Science.
- H. M. Pereira, F. F. Lima, B. M. Silva and A.F. Kohn (2020)
Sex differences in fatigability after ischemic preconditioning of non-exercising limbs.
Biology of Sex Differences.
- F. H. Magalhães, E. M. Mello and A. F. Kohn (2019)
Association Between Plantarflexion Torque Variability In Quiet Stance And During Force And Position Tasks.
Somatosensory & Motor Research.
- C.R. Silva, F.H. Magalhães and A.F. Kohn (2019)
Fingertip-Coupled Spindle Signaling Does Not Contribute to Reduce Postural Sway Under Light Touch.
Front. Physiol. 10:1072. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01072
- L. A. Elias, D. E. C. Matoso, R. N. Watanabe and A.F. Kohn (2018)
Perspectives on the modeling of the neuromusculoskeletal system to investigate the influence of neurodegenerative diseases on sensorimotor control.
Res. Biomed. Eng. vol.34 no.2.
- R. N. Watanabe and A.F. Kohn (2017)
Nonlinear frequency-domain analysis of the transformation of cortical inputs by a motoneuron pool-muscle complex.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NEURAL SYSTEMS AND REHABILITATION ENGINEERING, v. 25, p. 1-1.
- D.R. Toledo, J.A. Barela, A.F. Kohn (2017).
Improved proprioceptive function by application of subsensory electrical noise: Effects of aging and task-demand.
NEUROSCIENCE, v. 358, p. 103-114.
- D.R. Toledo, J.A. Barela, G.M. Manzano, A.F. Kohn (2016).
Age-related differences in EEG beta activity during an assessment of ankle proprioception
Neuroscience Letters - Volume 622, 27 May 2016, Pages 1–5.
- D.R. Toledo, G.M. Manzano, J.A. Barela, A.F. Kohn (2016).
Cortical correlates of response time slowing in older adults: ERP and ERD/ERS analyses during passive ankle movement.
Clinical Neurophysiology - Volume 127, Issue 1, January 2016, Pages 655–663.
- F.H. Magalhães, L.A. Elias, C.R. Silva, F.F. Lima, D.R. Toledo, A.F. Kohn (2015).
D1 and D2 Inhibitions of the Soleus H-Reflex Are Differentially Modulated during Plantarflexion Force and Position Tasks
PLoS ONE 10(11): e0143862. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0143862 (Nov 2015).
-
R. N. Watanabe and
A.F. Kohn (2015).
Fast Oscillatory Commands from the Motor Cortex Can Be Decoded by the Spinal Cord for Force Control.
The Journal of Neuroscience, 7 October 2015, 35(40): 13687-13697; doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1950-15.2015
- A.M.L. Nogueira, O.F.A. Bueno, G.M. Manzano, A.F. Kohn, S. Pompéia (2015).
Late positive slow waves as markers of chunking during encoding.
Front Psychol. 2015; 6: 1032
- A. R. Martinelli, D. B. Coelho, F.H. Magalhães, A.F. Kohn, L. A. Teixeira (2015).
Light touch modulates balance recovery following perturbation: from fast response to stance restabilization.
Experimental Brain Research - May 2015, Volume 233, Issue 5, pp 1399-1408
- R.A. Mezzarane, F.H. Magalhães, V.M. Chaud, L.A. Elias, A.F. Kohn (2015).
Enhanced D1 and D2 Inhibitions Induced by Low-Frequency Trains of Conditioning Stimuli: Differential Effects on H- and T-Reflexes and Possible Mechanisms.
PLoS ONE 10(3): e0121496. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121496
- L.A. Elias, R.N. Watanabe, A.F. Kohn (2014).
Spinal Mechanisms May Provide a Combination of Intermittent and Continuous Control of Human Posture: Predictions from a Biologically Based Neuromusculoskeletal Model.
PLoS Computational Biology - Volume 10, Issue 11, page e1003944.
- A.F. Kohn (2014).
Dissecting mechanisms behind force control in humans by a mixture of experimentation, mathematical analysis and computer simulations of neuronal models.
The Journal of Physiology - Volume 592, Issue 16, page 3341.
- L.A. Okai, A.F. Kohn (2014).
Quantifying the Contributions of a Flexor Digitorum Brevis Muscle on Postural Stability.
Motor Control - vol.:19 iss:3 pág.:161-172
- F.H. Magalhães, A.F. Kohn (2014).
Effectiveness of electrical noise in reducing postural sway: a comparison between imperceptible stimulation applied to the anterior and to the posterior leg muscles
European Journal of Applied Physiology - Volume 114, Issue 6, pp 1129-1141
- E.M. Mello, F.H. Magalhães, A.F. Kohn (2013). Larger plantar flexion torque variability implies less stable balance in the young: an association affected by knee position Human Movement Science 32 (6), 1310-1324
- R.N. Watanabe, F.H. Magalhães, L.A.
Elias, V.M. Chaud, E.M. Mello, A.F. Kohn (2013).
Influences of
premotoneuronal command statistics on the scaling of
motor output variability during isometric plantar
flexion Journal
of Neurophysiology 110 (11), 2592-2606
- L.A. Elias, A.F. Kohn (2013).
Web-based neuromuscular
simulator applied to the teaching of principles of
neuroscience . Revista Brasileira de Engenharia
Biomédica 29 (3), 213-226
-
R.A. Mezzarane, L.A. Elias, F.H. Magalhães, V.M Chaud and A.F. Kohn (2013). Experimental and Simulated EMG Responses in the Study of the Human Spinal Cord "Electrodiagnosis in New Frontiers of Clinical Research", book edited by Hande Turker, ISBN 978-953-51-1118-4, Published: May 22, 2013 under CC BY 3.0 license
-
F.H. Magalhães, D.R. Toledo and A.F. Kohn (2013). Plantar flexion force induced by amplitude-modulated tendon vibration and associated soleus V/F-waves as an evidence of a centrally-mediated mechanism contributing to extra torque generation in humans Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation 2013, 10:32
-
L.A. Elias and A.F. Kohn (2013). Individual and collective properties of computationally efficient motoneuron models of types S and F with active dendrites Neurocomputing - Volume 99, 1 January 2013, Pages 521–533
-
R. A. Mezzarane, A. F. Kohn, E. Couto-Roldan, L. Martinez, A. Flores and E. Majarrez (2012) Absence of effects of contralateral group I muscle afferents on presynaptic inhibition of Ia terminals in humans and cats Journal of Neurophysiology August 15, 2012 vol. 108 no. 4 1176-1185
-
L.A. Elias, V.M Chaud and A.F. Kohn (2012). Models of passive and active dendrite motoneuron pools and their differences in muscle force control Journal of Computational Neuroscience, December 2012, Volume 33, Issue 3, pp 515-531.
-
F.H. Magalhães and A.F. Kohn (2012). Imperceptible electrical noise attenuates isometric plantar flexion force fluctuations with correlated reductions in postural sway. Experimental Brain Research 2012 Mar;217(2):175-186. Epub 2011 Dec 24.
-
F.H. Magalhães and A.F. Kohn (2011). Vibratory noise to the fingertip enhances balance improvement associated with light touch. Experimental Brain Research 209, 139-151.
-
F.H. Magalhães and A.F. Kohn (2011). Vibration-enhanced posture stabilization achieved by tactile supplementation: May blind individuals get extra benefits? Medical Hypotheses. 2011 May 20.
-
P. H. Marchetti, A. F. Kohn and M. Duarte (2011). Selective activation of the rectus abdominis muscle during low-intensity and fatiguing tasks. Journal of Sports Science and Medicine(2011) 10, 322-327.
-
F.H. Magalhães and A.F. Kohn (2010). Vibration-induced extra torque during electrically-evoked contractions of the human calf muscles. Journal Neuroengineering and Rehabilitation, 7:26
-
R. A. Mezzarane and A. F. Kohn (2009) A method to estimate EMG crosstalk between two muscles based on the silent period following an H-reflex. Medical Engineering & Physics 31 (2009) 1331-1336
-
R. A. Mezzarane and A. F. Kohn (2008) Postural control during kneeling. Experimental Brain Research (2008) 187:395–405. DOI 10.1007/s00221-008-1308-x
-
M.C.S. Fornari and A.F. Kohn (2008). High frequency tendon reflexes in the human soleus muscle. Neuroscience Letters, v. 440, p. 193-196. DOI 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.05.075.
-
R.R.L. Cisi and A.F. Kohn (2008). Simulation system of spinal cord motor nuclei and associated nerves and muscles, in a web-based architecture. Journal of Computational Neuroscience, 25, 520-542. DOI 10.1007/s10827-008-0092-8.
-
R.A. Mezzarane and A.F. Kohn (2007). Control of upright stance over inclined surfaces. Experimental Brain Research, 180, 377-388.
-
M.F. Vieira and A.F. Kohn (2007). Compartmental models of mammalian motoneurons of types S, FR and FF and their computer simulation . Computers in Biology and Medicine, 37, 842-860.
-
A.F. Kohn(2006). Autocorrelation and Cross-correlation Methods . Wiley Encyclopedia of Biomedical Engineering, Ed. Metin Akay. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 23 pp.
-
A.F. Kohn (2005). Cross-correlation between EMG and center of gravity during quiet stance: theory and simulations. Biological Cybernetics, 93, 382-388.
-
E. Manjarrez, Z. Hernández-Paxtián and A.F. Kohn (2005). Spinal source for the synchronous fluctuations of bilateral monosynaptic reflexes in cats. Journal of Neurophysiology, 94, 3199-3210.
-
L.M. Lucchesi, S. Pompéia, G.M. Manzano, A.F. Kohn, J.C. Galduroz, O.F.A. Bueno and S. Tufik (2003). Flunitrazepam-induced changes in neurophysiological, behavioural and subjective measures used to assess sedation. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry, 27, 525-533.
-
A.F. Kohn e M.F. Vieira (2002). Optimality in the encoding/decoding relations of motoneurones and muscle units. Biosystems, 67, 113-119.
-
R.A. Mezzarane and A.F. Kohn (2002). Bilateral soleus H-reflexes in humans elicited by simultaneous trains of stimuli: symmetry, variability and covariance. Journal of Neurophysiology, 87, 2074-2083.
-
G.M. Manzano and A.F. Kohn (2000). Proximal receptors and the mechanical stimulation of the fingers: a somatosensory evoked potential study. Electromyography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 40, 21-29.
-
D.G. Goroso, R.R.L. Cisi and A.F. Kohn (2000). The amplitude and phase responses of the firing rates of some motoneuron models. Biosystems, 58, 33-39.
-
A. F. Kohn (1998). Effects of synaptic noise on a neuronal pool model with strong excitatory drive and recurrent inhibition. Biosystems, 48, 113-121.
-
A.F. Kohn, M.K. Floeter and M. Hallett (1997). Presynaptic inhibition compared with homosynaptic depression as an explanation for soleus H reflex depression in humans. Experimental Brain Research, 116, 375-380.
-
M. K. Floeter and A. F. Kohn (1997). H reflexes of different sizes exhibit differential sensitivity to low frequency depression. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology (Electromyography and motor control), 105, 470-475.
-
A. F. Kohn (1997). Computer simulations of noise resulting from random synaptic activities. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 27, 293-308.
-
A.F. Kohn, L.G.M. Nakano, M. Oliveira and Silva (1996). A class discriminability measure based on feature space partitioning. Pattern Recognition, 29, 873-887.
-
A.F. Kohn and S. S. Furuie (1991). Safety in medical signal analysis. Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine, IEEE, 10, pages 56 and 62.
-
A.F. Kohn (1989). A versatile waveform generator for testing neuroeletric signal processors. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 29, 157-163.
-
A.F. Kohn (1989). Dendritic transformations on random synaptic inputs as measured from a neuron's spike train - Modeling and simulation. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 36, 44-54.
-
A.F. Kohn (1987). Phase distortion in biological signal analysis caused by linear phase FIR filters. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, 25, 231-238.
-
O.D.Martinez, A.F.Kohn and J.P.Segundo (1983). Pervasive locking, saturation, asymmetric rate sensitivity and double- valuedness in crayfish strech-receptors. Biological Cybernetics, 49, 33-45.
-
A.F.Kohn and J.P.Segundo (1983). Neuromime and computer simulations of synaptic interactions between pacemakers. Mathematical expansions of existing models. Journal of Theoretical Neurobiology., 2, 101-125.
-
A.F.Kohn, A.F.Rocha and J.P.Segundo (1981). Presynaptic irregularity and pacemaker inhibition. Biological Cybernetics, 41, 5-18.
-
J.P.Segundo and A.F.Kohn (1981). A model of excitatory synaptic interactions between pacemakers. Its reality, its generality and the principles involved. Biological Cybernetics, 40, 113-126.
 Livro em pdf disponível para os interessados.
Clique
aqui
para fazer o download.
Livro em pdf disponível para os interessados.
Clique
aqui
para fazer o download.
Vozes da Engenharia Biomédica, 2024, uma entrevista à Sociedade Brasileiria de Engenharia Biomédica
Clique
aqui para acessar a entrevista.
WEBINAR - 45 ANOS DE SBEB
No dia 11 de maio de 2021, a Sociedade Brasileira de Engenharia Biomédica (SBEB) realizou um webinar em comemoração aos 45 anos da Instituição. O professor titular da Poli, André Fabio Kohn, foi um dos participantes do evento.
Clique
aqui para assistir o vídeo direto no Youtube.
Palestra proferida em português em outubro de 2020 no Congresso Brasileiro de Engenharia Biomédica
Clique
aqui para assistir o vídeo direto no Youtube.
Selected Conference Publications
- PIMENTA MARIANA T., SILVA CRISTIANO R da, KOHN, ANDRÉ F. Light touch increases muscle synergy coordination, reducing synergy space in quiet bipedal stance. Proceedings Volume 12924, Third International Conference on Biological Engineering and Medical Science (ICBioMed2023); 1292438 (2024)
- FREITAS, R. M. ; KOHN, ANDRÉ F. Quantitative and
qualitative parameters of myoelectric signals for computational
simulations of human surface electromyograms. In: 10th International
Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Technology, 2020, Toquio.
Proceedings of thje 2020 10th International Conference on Biomedical
Engineering and Technology. New York: ACM The Association for Computing
Machinery, 2020. p. 256-262.
-
URBIZAGASTEGUI, P. ; WATANABE, R. N. ; KOHN, ANDRÉ F . Influência das células de Renshaw na geração de força muscular. In: XXVII CBEB 2020, 2020, Vitória. Proceedings CBEB2020, 2020. p. 1-6.
-
SILVA, C. R. ; MAGALHÃES, F. H. ; KOHN, ANDRÉ F . Muscle receptors of a finger fail to contribute as expected to postural sway decrease during light touch. In: Congresso Brasileiro de Engenharia Biomédica, 2018, Buzios. Anais do CBEB. Rio de Janeiro: SBEB, 2018. p. 1-9.
- M. Gazola, R. N. Watanabe, H. Lee, H. I. Krebs, A.
F. Kohn and L. A. Elias (2017).
Passive ankle joint mechanical impedance investigaged with a musculoskeletal model. V Congresso Brasileiro de Eletromiografia e Cinesiologia, 2017, Uberlância. Anais do COBEC. Uberlandia: SBEB/UFU, p. 1-4.
- V.M Chaud and A.F. Kohn (2017)
Development of a User-Friendly Neuron Analyzer and Simulator (NAS).
European Modelling Symposium on Mathematical Modelling and Computer Simulation, 2017, Manchester. Annals of the EMG2017. New Jersey: IEEE, p. 1-6.
D. R. Toledo,
A.
F. Kohn, A. Gollhofer
and C. Leukel
(2017).
Corticospinal excitability changes following sensorimotor accuracy training performed with stochastic resonance stimulation.
Progress in Motor Control, 2017, Miami. PMC Abstracts2017, p. 221-222. - L.A. Elias, D. R. Toedo, F. F. de Lima and A.F. Kohn (2017).
The gain of visual feedback influences force variability but not corticomuscular coherence during plantarflexion isometrica contractions. Annual Meeting of the Society for Neuroscience, 2017, Washington. Abstracts of the SfN. Washington: Society for Neuroscience, p. 1-1.
- R. N. Watanabe and A.F. Kohn (2014).
System identification of a motor unit pool using a realistic neuromusculoskeletal model Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics - 5th IEEE RAS & EMBS International Conference. Sao Paulo, Brazil.
August 12-15, 2014. Page(s): 610-615
- V.M Chaud, L.A. Elias,
R. N. Watanabe and A.F. Kohn (2012).
A
simulation study of the effects of activation-dependent
muscle stiffness on proprioceptive feedback and
short-latency reflex The Fourth IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference
on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics. Roma, Italy.
June 24-27, 2012. Page(s): 133 - 138
- L. A. Elias and A. F. Kohn
(2010)
Single
neuron
and
network models in force control. In: 9th Neural
Coding Workshop, Limassol.
- A.F. Kohn (2009). Force fluctuations in a simulated motoneuron pool - World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Munich, Germany, IFMBE Proceedings 25/IX, pp. 197–200.
-
R.R.L. Cisi and A.F. Kohn (2008). From neuronal ionic channels to muscle control: a Web-based simulator and its application to teaching. World Congress of Engineering /International Conference on Systems Biology and Bioengineering. London, pp 1-4.
- R.R.L. Cisi and A.F. Kohn (2007).
H-reflex
depression simulated by a biologically realistic
motoneuron network. 29th Annual International
Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology
Society, Lyon, France, 4 pages in CD-ROM.
-
A.F. Kohn (2007). Estimation of neural noise spectrum in a postural control model. IFMBE Proceedings, vol. 16, of the 11th Mediterranean Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering (Ljubljana, Slovenia), 419-422.
-
L.A. Okai e A.F. Kohn (2006). The influence of the flexor digitorum brevis muscle on postural stability. XVI Congress of the International Society of Electrophysiology and Kinesiology (Torino, Italy), pp 1.
- L.A. Okai and A.F. Kohn (2005). Effects of contractions of the flexor digitorum brevis muscle on postural stability. Progress in Motor Control V (State College, PA, USA), pp. 23 section 1.
-
R.R.L.Cisi and A.F. Kohn (2004). Spinal Cord Neuronal Network Simulator. Proceedings of the 28th Conference of the Canadian Medical and Biological Engineering Society (Quebec, Canadá), CD-ROM, pp 1-3.
-
A.F. Kohn, M. K. Floeter and M. Hallett (1995). A model-based approach for the quantification of H reflex depression in humans. 17th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (Montreal, Canada).
Teaching at the University of Sao Paulo
Over the years I have taught undergraduate and graduate courses on: Signals and Systems, Digital Signal Processing, Biological Signal Processing, Introduction to Stochastic Processes, Fundamentals of Neuroscience, Computational Neuroscience, Spinal Cord Neurophysiology, Neurophysiology of Motor Control, Analysis of Random Signals, Statistical Pattern Recognition.
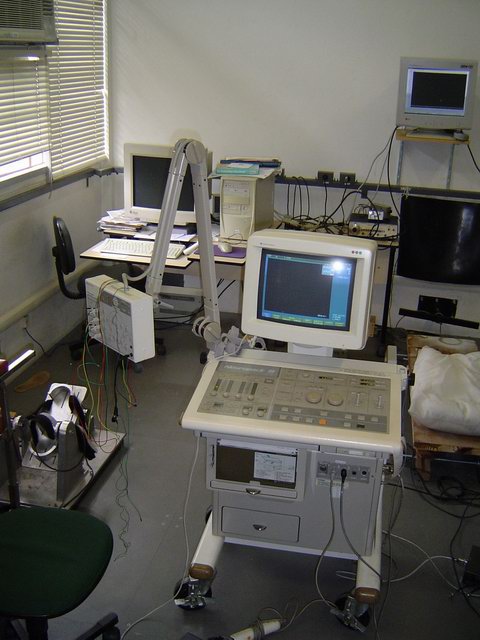


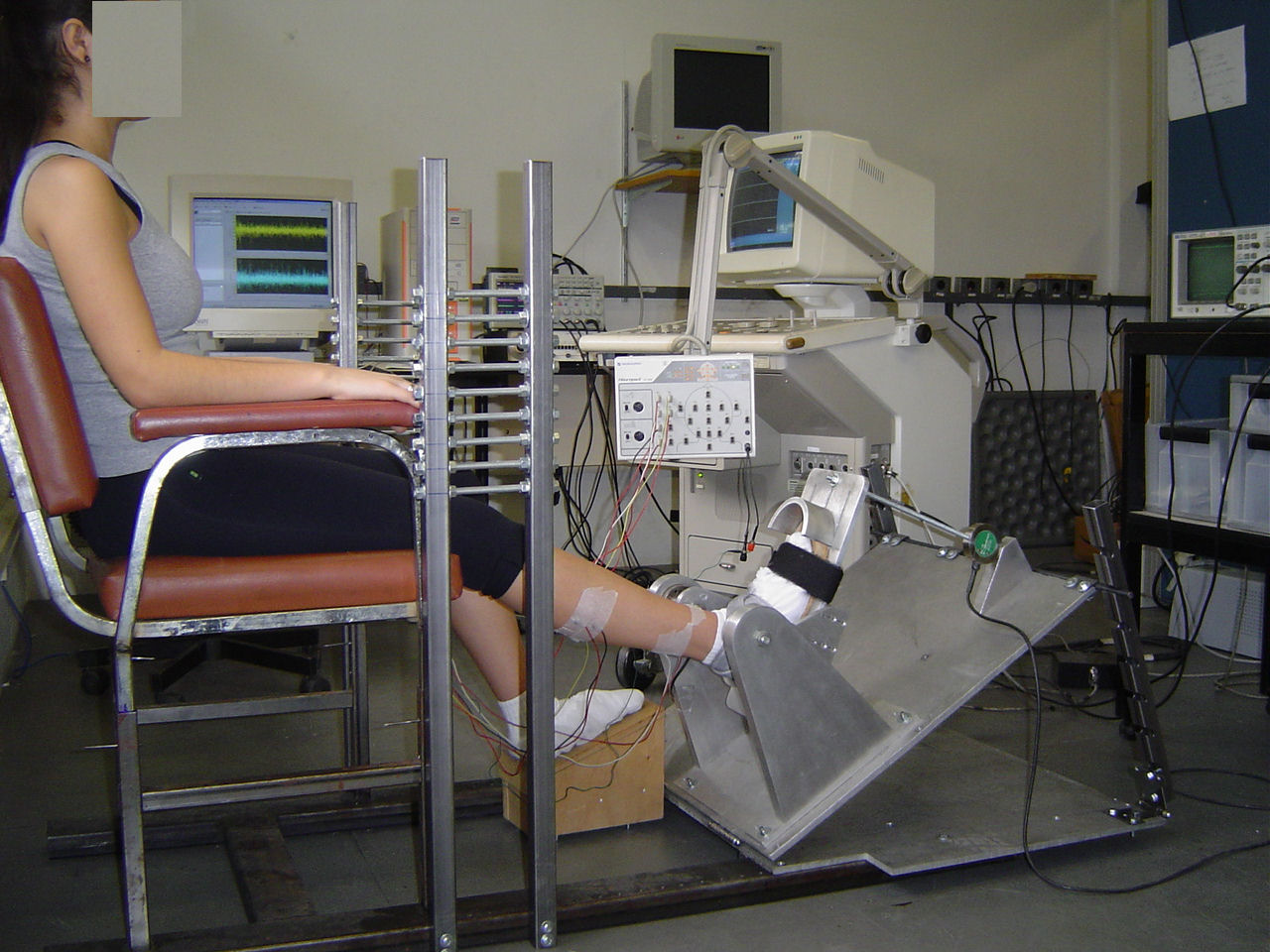
pictures taken from
our neurophysiology lab
Miscellany
Recipient of the Ralph Crump
Award for Excellence in Medical Engineering at
UCLA in 1980. Member of the CNPq
(Brazilian N.S.F.) National Committee for Electrical and
Biomedical Engineering from 1991 to 1993 and 2005 to 2007.
Member of Scientific Committees of national and
international Conferences on Biomedical Engineering and
Neuronal Modeling.
Hobbies
Eco-travel
to wonderful forests, mountains, waterfalls and
beaches in Brazil.
Watching/listening DVDs and CDs (pop/rock,
classical, jazz), reading books, barbecue activities.
Address
andfkohn@leb.usp.br
andkohn@usp.br
Universidade de São Paulo,
Escola Politécnica, PTC
Cx.P. 61548
CEP 05424-970, São Paulo, S.P., Brasil
-------------------------------------------------------------
or (a non-post office box address):
Universidade
de São Paulo,
Escola Politécnica, PTC
Av. Prof. Luciano Gualberto, Trav 3, 158
CEP 05508-900, São Paulo, S.P., Brasil
-------------------------------------------------------------
or if you come personally:
room D2-09 of block D
at the Electrical Engineering
Building
Av. Prof. Luciano Gualberto, trav. 3, 158.
Cidade Universitária - CEP 05586-0600
São Paulo, SP, Brasill